On this page, we will provide a general overview of the “Economy of Indonesia”. This article is an introduction to other articles that are more specific about economic conditions in Indonesia. A more detailed discussion will focus on how the economic conditions are affecting society in Indonesia. Because Indonesia has very diverse societal characteristics, it will also show a variety of economic conditions that will be described.
See Table of Contents
Introduction to the Economy of Indonesia
Welcome to our overview of the economy of Indonesia. In this article, we will provide a general introduction to the economic conditions in Indonesia. This serves as a foundation for more specific discussions on how these conditions are affecting society in the country. Due to Indonesia’s diverse societal characteristics, we will also explore the various economic conditions that exist within the nation. You can also read about “Economy of Indonesia” on other websites such as Wikipedia.
The Economic Landscape of Indonesia
Indonesia, located in Southeast Asia, is the world’s fourth most populous country and has a rapidly growing economy. With its abundant natural resources, strategic geographical location, and a young and dynamic workforce, Indonesia has become an attractive destination for investors and businesses.
Indonesia’s economy is a complex and multifaceted system, primarily driven by its manufacturing, agriculture, and services sectors. This blog post delves into the significant contributions of these sectors to the country’s economic landscape.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector in Indonesia is a cornerstone of its economy. The country is known for producing a diverse range of goods, including textiles, automotive parts, and electronics. These industries not only cater to domestic consumption but also hold substantial export value. Indonesia’s robust manufacturing sector is a critical driver of employment and economic growth.

Agricultural Sector
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in Indonesia’s economy, with the country being one of the largest producers of rice, palm oil, and rubber. The agricultural sector not only sustains a significant portion of the population but also contributes extensively to export revenues. Palm oil, in particular, stands out as a major export commodity, positioning Indonesia as a leading player in the global market.

Services Sector
The services sector in Indonesia is rapidly expanding, encompassing various industries such as finance, tourism, and telecommunications. This sector is essential for economic diversification and resilience, providing a broad spectrum of employment opportunities. The growth of the services sector underscores Indonesia’s shift towards a more balanced and sustainable economic model.
In recent years, the services sector has witnessed significant growth, encompassing areas such as tourism, finance, and telecommunications. This expansion reflects broader economic trends and strategic interventions aimed at fostering a conducive business environment.
Government Policies Promoting Investment
The government has played a pivotal role in the development of the services sector. By implementing various policies designed to attract investment, authorities have managed to create a favorable climate for business. These initiatives have not only bolstered domestic enterprises but also attracted substantial foreign direct investment (FDI).
Tourism: A Thriving Industry
Tourism has emerged as a cornerstone of the services sector, contributing significantly to economic growth. Government efforts to promote the country as a tourist destination have resulted in increased visitor numbers and revenue, thereby supporting local businesses and communities.
Finance: A Catalyst for Economic Development
The finance sector has also experienced remarkable growth, facilitated by regulatory reforms and technological advancements. These changes have enhanced financial services and accessibility, enabling better support for both individuals and enterprises.
Telecommunications: Connecting the Nation
Telecommunications has seen rapid advancements, driven by increased demand for connectivity and digital services. Investments in infrastructure and innovation have improved communication networks, benefiting consumers and businesses alike.
The growth of the services sector, supported by strategic government policies, has led to increased foreign direct investment and overall economic development. As tourism, finance, and telecommunications continue to expand, they will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in shaping the future economic landscape.
In summary, the economic landscape of Indonesia is significantly shaped by its manufacturing, agriculture, and services sectors. Each of these sectors contributes uniquely to the country’s economic stability and growth. Understanding these pillars provides valuable insights into Indonesia’s economic dynamics and future potential.
The Impact of Economic Conditions on Indonesian Society
The economic conditions in Indonesia have a profound impact on society as a whole. The country’s economic growth has led to improvements in living standards, increased access to education and healthcare, and reduced poverty rates. However, challenges such as income inequality, unemployment, and environmental sustainability persist.
One of the key issues facing Indonesian society is income inequality. While the country has experienced significant economic growth, the benefits have not been evenly distributed. The gap between the rich and the poor remains wide, with a significant portion of the population still living in poverty. Efforts are being made to address this issue through social welfare programs and initiatives to promote inclusive economic growth.
The Current State of Income Inequality in Indonesia
Income inequality in Indonesia has been a persistent issue despite the nation’s economic growth over the past few decades. The Gini coefficient, a measure of inequality, indicates that income distribution remains highly uneven. This disparity has significant social and economic implications, necessitating urgent attention from policymakers and stakeholders.
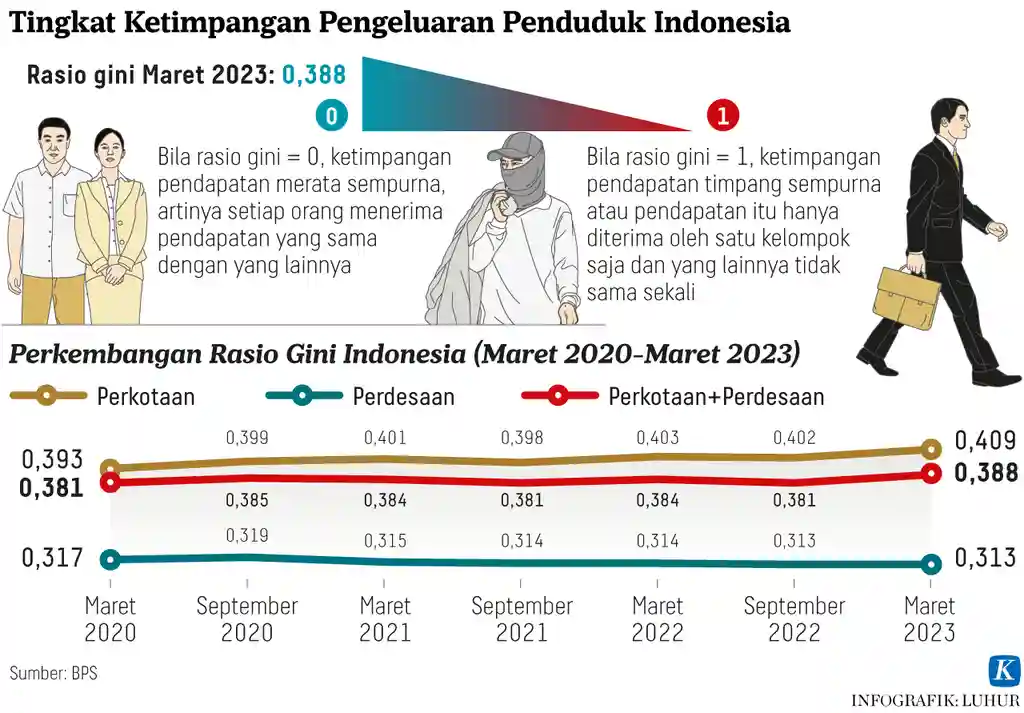
Causes of Income Inequality
Several factors contribute to income inequality in Indonesia. Firstly, the disparity in education quality and access creates a significant gap in employment opportunities. Urban areas, particularly Jakarta, offer more lucrative jobs compared to rural regions. Secondly, the informal sector, which employs a large portion of the population, tends to pay lower wages without job security. Additionally, economic policies favoring capital-intensive industries over labor-intensive ones exacerbate the income gap.
Impact on Society
The consequences of income inequality extend beyond economic metrics. Social cohesion is threatened as the gap between the rich and poor widens, leading to increased social tensions and potential unrest. Public health can also suffer, as lower-income households may lack access to adequate healthcare. Education disparities further entrench inequality, creating a cycle that is difficult to break.
Addressing the Issue
To mitigate income inequality in Indonesia, comprehensive and multifaceted strategies are necessary. Improving access to quality education across all regions, investing in rural development, and promoting labor-intensive industries can create more equitable opportunities. Social protection programs, such as conditional cash transfers, can help alleviate poverty and reduce vulnerability. Furthermore, progressive taxation and better governance are crucial in redistributing wealth and ensuring sustainable economic development.
In conclusion, addressing income inequality in Indonesia requires a concerted effort from all sectors of society. By implementing inclusive policies and fostering equitable growth, the nation can work towards a more balanced and prosperous future for all its citizens.
The Unemployment Issue
Unemployment is another challenge that Indonesia faces. Despite the growing economy, job creation has not kept pace with the expanding workforce. This has resulted in a high unemployment rate, particularly among young people. The government is working to address this issue by promoting entrepreneurship, vocational training, and investment in sectors with high employment potential.

Unemployment is a significant challenge that Indonesia continues to face. Despite being Southeast Asia’s largest economy, the country struggles with high unemployment rates, impacting its socio-economic fabric. Understanding the underlying causes and potential solutions is crucial for sustainable development.
Current State of Unemployment
Indonesia’s unemployment rate has seen fluctuations over the years. Factors such as economic downturns, inadequate education and training, and rapid population growth contribute to this issue. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated the situation, leading to job losses across various sectors.
Government Initiatives and Policies
The Indonesian government has implemented several initiatives to combat unemployment. Programs aimed at enhancing vocational training, promoting entrepreneurship, and attracting foreign investments have shown promise. However, these measures require consistent evaluation and adaptation to meet the dynamic needs of the labor market.
The Role of Education and Skill Development
Education and skill development are pivotal in addressing unemployment. By aligning educational curricula with industry demands, Indonesia can create a workforce that is better equipped for available job opportunities. Collaborative efforts between educational institutions and industries can bridge the skill gap and reduce unemployment rates.
Conclusion on the problem of unemployment
Tackling unemployment in Indonesia is a multifaceted challenge that requires concerted efforts from the government, private sector, and educational institutions. By focusing on comprehensive strategies, Indonesia can pave the way for a more resilient and inclusive economy, ultimately improving the livelihoods of its citizens.
Economic Pressure on the Environment
Indonesia has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades, significantly improving the standards of living for many of its citizens. However, this growth has also put substantial pressure on the environment, leading to issues such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. It is crucial to address these concerns to ensure sustainable economic development.
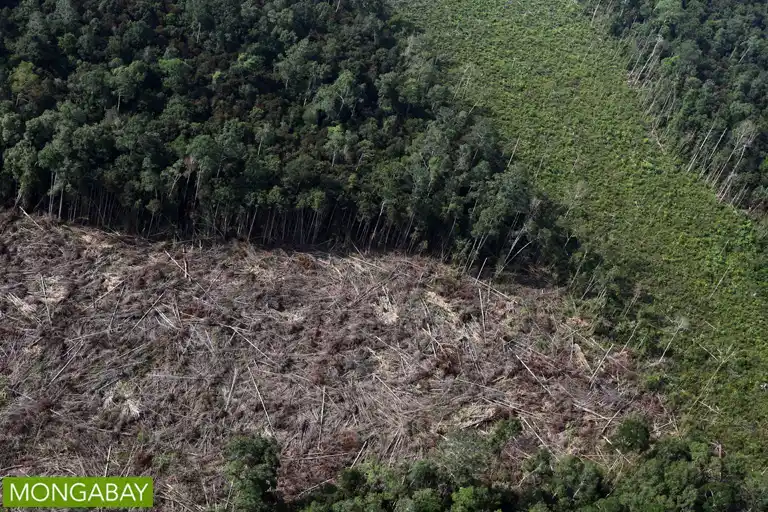
Environmental Challenges
Deforestation in Indonesia is a major concern, primarily driven by agricultural expansion, logging, and infrastructure development. This loss of forest cover not only threatens biodiversity but also contributes to carbon emissions. Additionally, pollution from industrial activities and urbanization has deteriorated air and water quality, affecting public health and ecosystems. Climate change poses another significant threat, with increasing temperatures and changing weather patterns impacting agriculture and coastal communities.

Government Initiatives
In response to these environmental challenges, the Indonesian government has implemented various policies and initiatives aimed at promoting environmental conservation and reducing carbon emissions. Programs such as the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) initiative focus on conserving forests and promoting sustainable land use practices. The government has also introduced regulations to control pollution and encourage the use of renewable energy sources.
Conclusions about Economic Pressure on the Environment
While Indonesia’s economic growth has brought numerous benefits, it is imperative to balance this growth with environmental sustainability. By addressing deforestation, pollution, and climate change through effective policies and initiatives, Indonesia can pave the way for a more sustainable future. Continued efforts and collaboration among government, industry, and communities will be essential in achieving this balance.
Diverse Economic Conditions in Indonesia
Given Indonesia’s vast geographical and cultural diversity, the country exhibits a wide range of economic conditions. While some regions and communities have experienced rapid economic growth, others continue to face significant challenges.
Economic conditions in urban areas
In Indonesia, urban areas like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bali are experiencing pronounced economic development. Serving as primary economic hubs, these cities attract significant investments, businesses, and tourists. This post explores how these urban centers contribute to the nation’s overall economic growth and the wide range of job opportunities they offer.
Jakarta: The Economic Powerhouse
Jakarta, the capital city of Indonesia, stands as the nation’s primary economic powerhouse. With a diverse economy driven by finance, manufacturing, and services, Jakarta attracts both local and international investments. The city’s well-developed infrastructure and strategic location make it a desirable destination for businesses aiming to establish a presence in Southeast Asia. As a result, Jakarta offers numerous job opportunities across various sectors.
Surabaya: A Growing Industrial Hub
Surabaya, Indonesia’s second-largest city, is rapidly growing as an industrial hub. The city’s strategic position on the island of Java makes it an ideal location for manufacturing and trade. Surabaya’s port is one of the busiest in the country, facilitating the flow of goods and contributing to economic growth. The city’s robust industrial sector provides a myriad of employment opportunities, attracting a skilled workforce from across the nation.
Bali: Tourism and Beyond
Bali is globally renowned for its tourism industry, which significantly contributes to the island’s economic development. However, beyond tourism, Bali is also seeing growth in sectors such as retail, real estate, and creative industries. The influx of tourists drives demand for various services, creating jobs and fostering economic diversification. Bali’s appeal as a tourist destination also attracts investments in infrastructure and hospitality, further boosting the local economy.
Conclusions about economic conditions in urban areas
Urban areas like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bali are pivotal to Indonesia’s economic development. Their ability to attract investments, businesses, and tourists not only drives local growth but also contributes significantly to the country’s overall economic progress. These cities offer diverse job opportunities, making them attractive destinations for professionals and entrepreneurs alike.
Economic conditions in rural areas
Economic conditions in rural areas and remote islands can often be less favorable compared to urban centers. Limited access to infrastructure, education, and healthcare services plays a significant role in hindering economic development. This blog post explores the various challenges faced by these communities and highlights potential opportunities for improvement.

Challenges in Rural Economies
One of the primary challenges in rural areas is the dependency on agriculture as the main source of income. Low productivity, limited market access, and vulnerability to climate change exacerbate the economic instability that many rural communities experience. The lack of modern infrastructure further restricts their ability to grow and diversify their economies.
Limited Access to Essential Services
Access to essential services such as education and healthcare is often limited in these areas. Poor educational facilities hinder the development of a skilled workforce, reducing the potential for economic growth and innovation. Likewise, inadequate healthcare services can lead to higher rates of illness and mortality, further straining the community’s economic resources.
Opportunities for Improvement
Despite these challenges, there are several opportunities to enhance the economic conditions in rural and remote areas. Investing in infrastructure development can provide better access to markets, education, and healthcare services. Additionally, implementing sustainable agricultural practices can improve productivity and resilience to climate change. By addressing these key areas, rural communities can unlock their economic potential and improve their overall quality of life.
Conclusion about economic conditions in rural areas
While rural and remote areas face significant economic challenges, there are viable pathways to fostering development and growth. By focusing on infrastructure, education, healthcare, and sustainable agriculture, these communities can overcome obstacles and create a more prosperous future.
It is essential to understand and address the diverse economic conditions in Indonesia to ensure inclusive and sustainable economic growth across the country. The government has implemented various programs and policies to promote regional development and reduce disparities.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s economy is dynamic and rapidly growing, driven by its manufacturing, agriculture, and services sectors. The economic conditions in the country have a significant impact on society, with both positive and negative consequences. Income inequality, unemployment, and environmental sustainability are among the challenges that Indonesia faces.
As we delve deeper into the topic of the economy of Indonesia in subsequent articles, we will explore specific aspects such as the role of government policies, the impact of globalization, and the potential for sustainable development. Stay tuned for more in-depth discussions on how the economy of Indonesia shapes society and its future prospects.
That is our review of “Economy of Indonesia“. We hope this can broaden your insight regarding Indonesia. Thank you for reading our website, “Indonesia Overview“.
Other articles about Economy of Indonesia
The following are several links to other articles discussing “Economy of Indonesia”. Articles that have been published will automatically appear in the following list. You can also find articles related to economics in the “Economy and Business” category.
